- Home
- Documentation
- Community
- Projects
- Boards
- Agilex 5 SoC
- Agilex 7 SoC
- Arria 10 SoC
- Nallatech 385A - Arria 10 FPGA Network Accelerator Card
- Nallatech 385A-SoC Accelerator Card with Arria 10 FPGA
- ALARIC Instant DevKit ARRIA 10 SoC FMC IDK by REFLEX CES
- Altera Arria 10 SoC Virtual Platform
- Altera Arria 10 SoC Board
- Nallatech 510T compute acceleration card with Intel Arria 10 FPGA
- REFLEX CES Achilles Arria 10 SoC SOM
- Terasic Arria10 SoC Board : HAN Pilot Platform
- Arria V SoC
- Cyclone V SoC
- Altera Cyclone V SoC Board
- Arrow SoCKit User Manual - July 2017 Edition
- Arrow SoCKit User Manual - November 2019 Edition
- Arrow SoCKit Evaluation Board
- Atlas-SoC Development Platform
- Critical Link MitySOM-5CSx Development Kit
- Cyclone V Ethernet driver problems
- DE10-Nano Development Board
- Terasic DE10-Standard Development Kit
- Devboards DBM-SoC1 module
- Devboards DBM-SoC2 module
- EBV SoCrates Evaluation Board
- Enclustra Mercury SA1 SoC Module
- Enterpoint Drigmorn 5
- Enterpoint Larg 2
- Altera Cyclone V SoC Development Platform
- Mpression Helio SoC Evaluation Kit by Macnica
- Mpression Sodia Evaluation Board by Macnica
- ARIES Embedded - MCV System on Module
- Mpression Borax SOM Module and Development Kit by Macnica
- Enterpoint Mulldonoch 3
- Networked Pro-Audio FPGA SoC Development Kit by Coveloz
- NOVPEK™CVLite
- NOVSOM®CV
- NOVSOM®CVLite
- NovTech IoT Octopus™
- NovTech NetLeap™
- Enterpoint Raggedstone 4
- Solectrix SMARC compliant System-on-Module
- Terasic DE1-SoC Development and Education Board
- Stratix 10 SoC
- Find a Board
- News
Documentation
Similar topics
-
 Linux Kernel Debugging With DS-5
Debug Linux kernel and drivers over JTAG using ARM DS 5 Intel SoC FPGA Edition
Linux Kernel Debugging With DS-5
Debug Linux kernel and drivers over JTAG using ARM DS 5 Intel SoC FPGA Edition -
Linux 13.02 - BSP User Manual
User Manual for Altera Linux Release 13.02
-
Linux 13.02 - Release Notes
Release Notes for Altera Linux 13.02
- How to compile,update and boot kernel
-
Altera Cyclone V SoC Development Platform
iW RainboW G17D Altera Cyclone V SoC Development Platform
Recent Changes
-
 Macnica Sulfur ~ Development Kit for Agilex™ 5 FPGA E-Series ~
Macnica Sulfur ~ Development Kit for Agilex™ 5 FPGA E-Series ~
-
 Building Bootloader for Agilex 5
Building latest bootloaders for Agilex 5 SoC Devices
Building Bootloader for Agilex 5
Building latest bootloaders for Agilex 5 SoC Devices - Ashling RiscFree Examples
-
 GSRD for Agilex 7 I-Series Transceiver-SoC DevKit (4x F-Tile)
Golden System Reference Design for DK SI AGI027FB, DK SI AGI027FA and DK SI AGI027FC
GSRD for Agilex 7 I-Series Transceiver-SoC DevKit (4x F-Tile)
Golden System Reference Design for DK SI AGI027FB, DK SI AGI027FA and DK SI AGI027FC -
Intel® Simics® Simulator for Intel FPGAs Release Notes
This page provides release information about the Intel® Simics® simulator for Intel FPGAs.
Table of Contents
Debug Linux applications over Ethernet using ARM DS-5 Intel SoC FPGA Edition
Debug Linux applications over Ethernet using ARM DS-5 Intel SoC FPGA Edition
Introduction
ARM DS-5 Intel SoC FPGA Edition enables you to debug Linux applications. This page presents and example of creating, compiling and running a simple Linux example application.Prerequisites
The following were used to create this example:- Host computer running Ubuntu 14.04LTS - other versions may work too
- SoC EDS Pro Edition v18.1 - for the ARM DS-5 SoC FPGA Edition
- S10 SoC Development Kit with:
- OOBE HPS Daughter Card
- QSPI SDM Flash Card
Configure Linux
In order to perform Linux application debugging, Linux needs to be running on your target board. Use the Getting Started page to select the appropriate instructions on how to make that work on your board. The following requirements are also needed: 1. The Linux running on the target needs to have the following packages included:- openssh-sftp-server (or another compatible version of sftp-server)
- gdbserver
passwd command.
3. On the Linux console, run the command ifconfig to determine the IP address of the board.
Import Sample Application
1. Start an Embedded Command shell:~/intelFPGA_pro/18.1/embedded/embedded_command_shell.sh2. Start ARM DS-5 Eclipse:
eclipse &3. In Eclipse, select File > Import. 4. In the Import dialog box, select General > Existing Projects into Workspace and click Next.
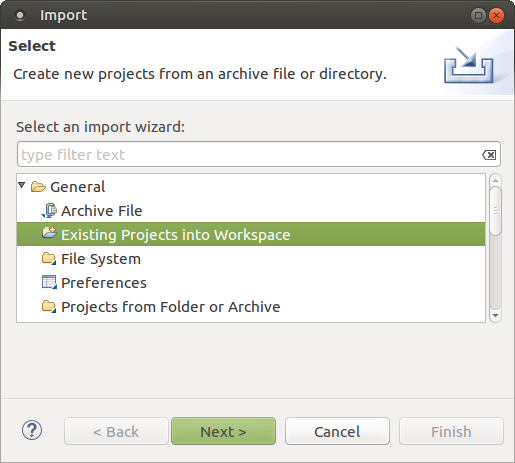 5. In the Import Projects dialog box, select the Select Archive File option.
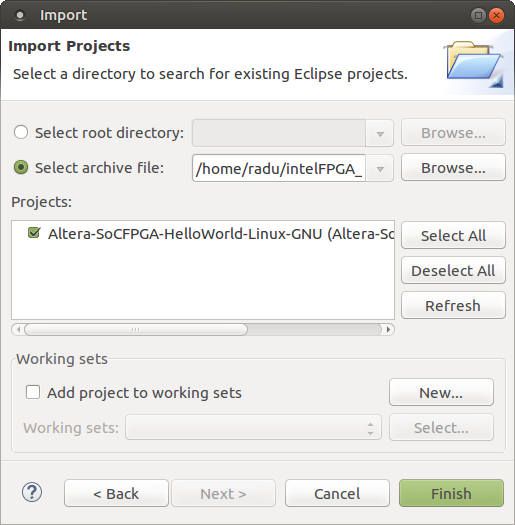
6. Click Browse, then navigate to ~/intelFPGA_pro/18.1/embedded/examples/software, select the file Altera-SoCFPGA-HelloWorld-Linux-GNU.tar.gz and click OK.
5. In the Import Projects dialog box, select the Select Archive File option.
6. Click Browse, then navigate to ~/intelFPGA_pro/18.1/embedded/examples/software, select the file Altera-SoCFPGA-HelloWorld-Linux-GNU.tar.gz and click OK.
Update Sample Application
The sample application provided with SoC EDS targets Cortex-A9 devices from CV/AV/A10 SoCs. It needs to be updated in order to be ran on the Cortex-A53 from S10 SoC. 1. Open the Makefile file by double-clicking it on the left panel in Eclipse. 2. Change the file to make it create a 64bit executable for Cortex-A53: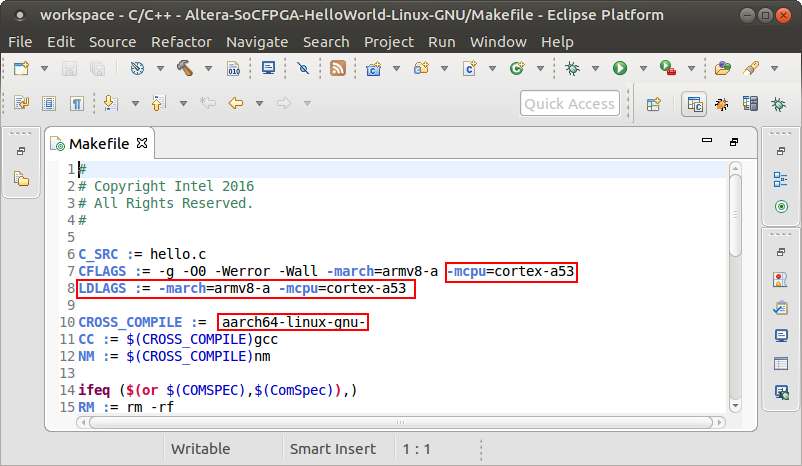
Compile Sample Application
1. Select the project in Project Explorer. 2. Select Project > Build Project or press CTRL-B. 3. The project compiles and the Project Explorer shows the newly created hello executable file as shown in the figure below. The Console dialog box shows the commands and responses that were executed.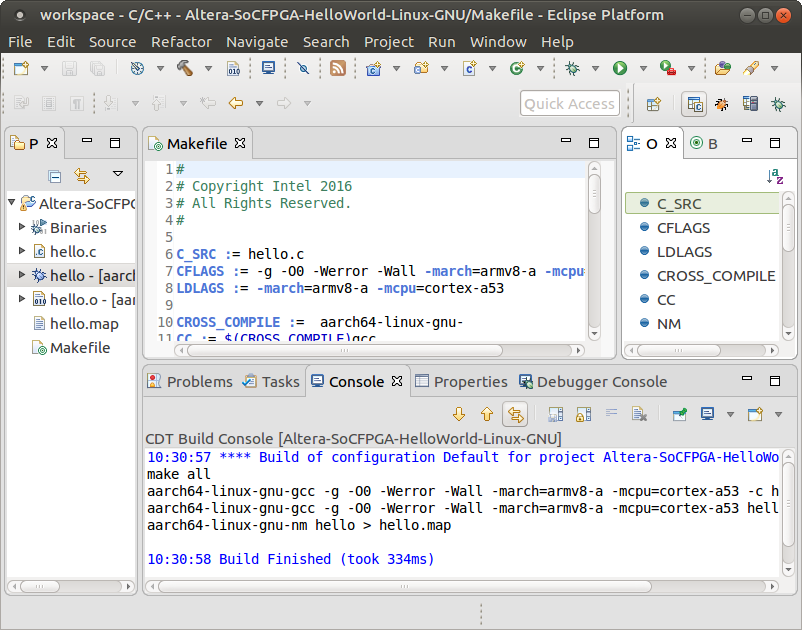
Setup Remote System Explorer
The ARM DS-5 AE can run and debug programs directly on the target with the help of the Remote System Explorer (RSE). Before this feature can be used, the RSE needs to be configured to connect to the target board running Linux. 1. In your Eclipse workspace, select Window > Open Perspective > Other. 2. In the Open Perspective dialog box, click the Remote System Explorer and click OK.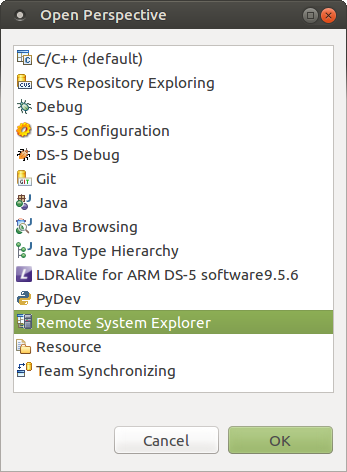 3. In the Remote System Explorer view, right click Local and select New > Connection …. Note that clicking the + sign achieves the same result.
3. In the Remote System Explorer view, right click Local and select New > Connection …. Note that clicking the + sign achieves the same result.
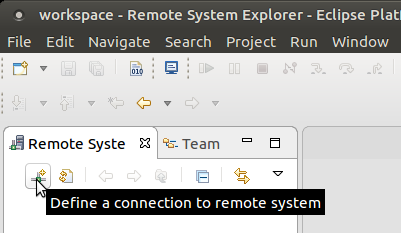 4. In the first page of the New Connection wizard, named Remote System Type, select SSH only and click Next.
4. In the first page of the New Connection wizard, named Remote System Type, select SSH only and click Next.
 5. Enter the IP address of the board in the Host Name field. Click Finish to create the connection.
5. Enter the IP address of the board in the Host Name field. Click Finish to create the connection.
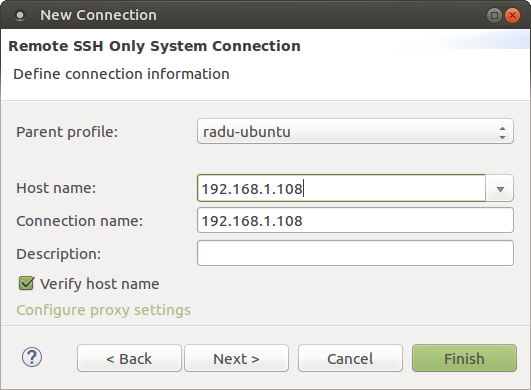 6. In the Remote Systems panel, click the Target IP > Sftp Files > Root. This opens a dialog box to enter the username and password. Enter 'root' as username and the password you have configured on the board.
6. In the Remote Systems panel, click the Target IP > Sftp Files > Root. This opens a dialog box to enter the username and password. Enter 'root' as username and the password you have configured on the board.
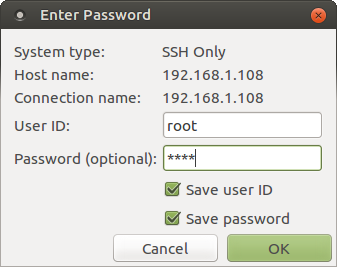 7. Eclipse asks for confirmation of authenticity of the board. Click Yes.
8. Remote System Explorer shows the files on the board on the left pane.
7. Eclipse asks for confirmation of authenticity of the board. Click Yes.
8. Remote System Explorer shows the files on the board on the left pane.
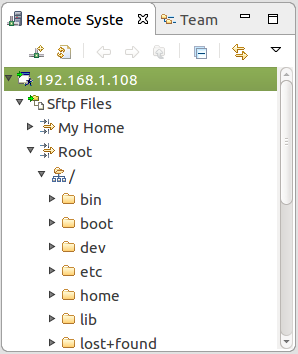
Debug Sample Application
At this stage, we have a compiled Linux application and a properly configured Remote Systems Connection. This section shows how to create a Debugger Configuration and use it to run and debug the application. 1. Select Run > Debug Configurations… 2. In the Debug Configurations dialog box right click the DS-5 Debugger and click New to create a new debug configuration. 3. Name the newly created debugger configuration, DebugLinuxHello, by editing its name in the Connection tab. 4. In the Connection tab, select:- For the Free Web Edition license, select Generic > gdb server > Linux Application Debug > Download and Debug Application
- For the Subscription Edition or 30-day Evaluation Edition, select Intel > Stratix 10 > Linux Application Debug > Download and Debug Application.
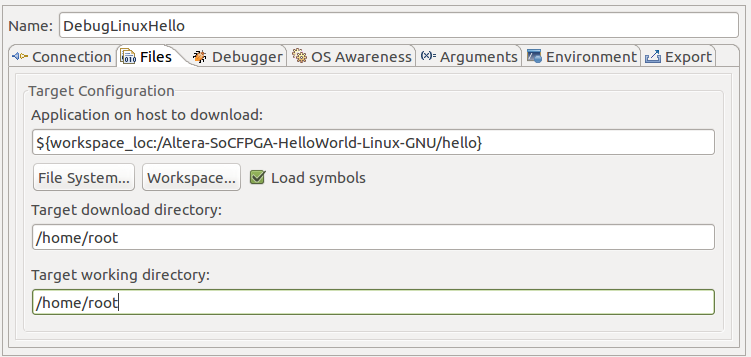
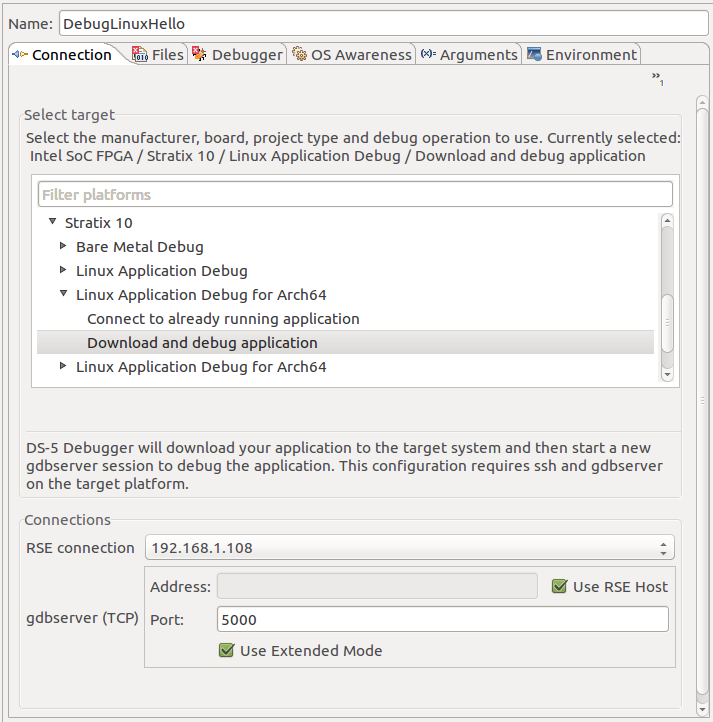 6. Go to Files tab, and set the Target Configuration parameters:
6. Go to Files tab, and set the Target Configuration parameters: - Select the Application on host to download to be the hello executable file. Use the Workspace… browse button.
- Edit the Target download directory to be /home/root.
- Edit the Target working directory to be /home/root.
 7. Click the Debug button. A dialog window appears asking to switch to Debug perspective. Click Yes.
8. Eclipse downloads the application to the board and stops upon entering the main function.
7. Click the Debug button. A dialog window appears asking to switch to Debug perspective. Click Yes.
8. Eclipse downloads the application to the board and stops upon entering the main function.
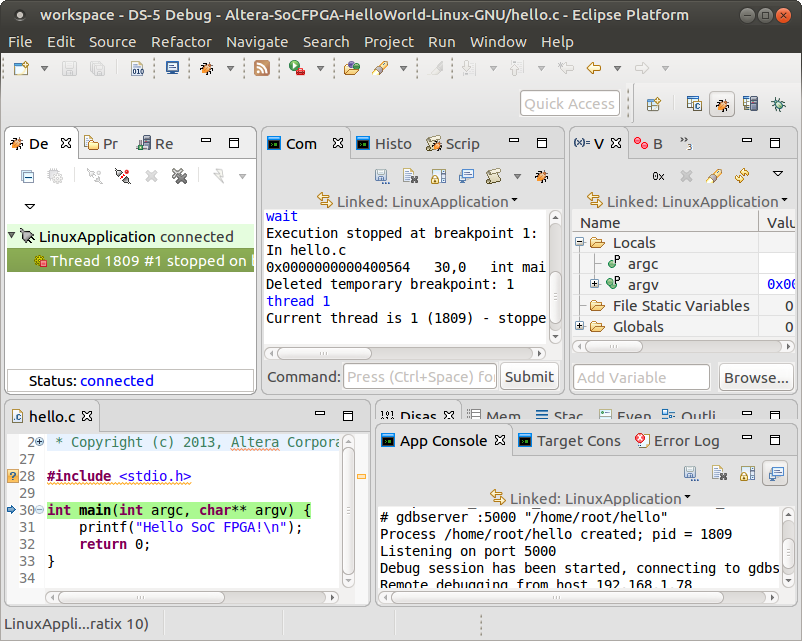 At this stage, all the usual debugging features of DS-5 can be used, such as breakpoints, view variables, registers, tracing, and threads.
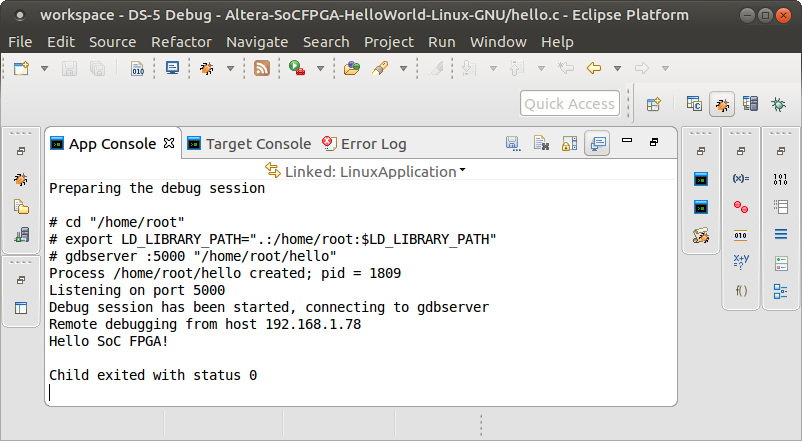
9. Click the Continue green button or press F8 to run the application. The hello message is printed on the Application Console.
At this stage, all the usual debugging features of DS-5 can be used, such as breakpoints, view variables, registers, tracing, and threads.
9. Click the Continue green button or press F8 to run the application. The hello message is printed on the Application Console.
© 1999-2024 RocketBoards.org by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors.
This website is using cookies. More info.
That's Fine
 RocketBoards
RocketBoards